MRI images are created without the use of ionising radiation, so patients are not exposed to the harmful effects of ionising radiation. Although there are no known health risks from transient exposure to the MR environment, the MR environment carries a high level of static electricity. Magnetic field, a magnetic field that changes over time (pulsed gradient field), and radio frequency energy, each with specific safety concerns. Most clinical magnets are superconducting magnets that require liquid helium. Due to the potential hazards associated with MRI, anyone entering the MRI environment must be trained or screened. Patients should undergo a thorough evaluation to ensure an appropriate MRI procedure. 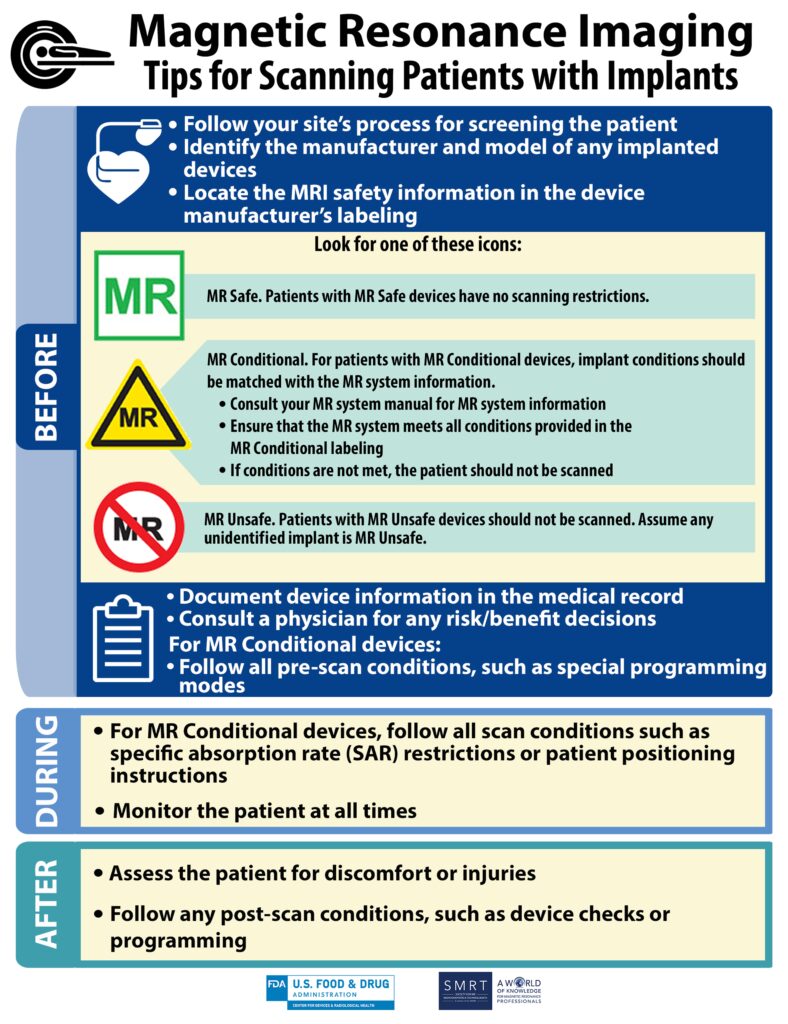
MRI Safety Considerations
- Ferromagnetic objects (e.g. steel, iron) are strongly attracted to the magnet and can become deadly projectiles. People can be seriously injured and equipment damaged if struck by objects that are attracted to the magnet at high speed. Life-threatening situations can arise with MRI machines if a person is pinched by a large ferromagnetic object on the magnet.
- Absolutely no ferromagnetic objects are allowed in a magnet room or within the specified radius of the magnetic field. You can test the magnetic susceptibility of objects with a handheld magnet.
- Examples of objects that should now no longer input the magnetic subject or room are ordinary extinguishers, air tanks, axes, guns, radios, flashlights, wheelchairs, MRI-compatible stretchers, and defibrillators. Smaller steel objects like badges, jewellery, watches, keys, dentures, glasses, listening aids, and hair clips should additionally be eliminated earlier than someone sporting them enters the magnet room or magnetic subject. Money cards and media devices may be destroyed with the help of using the subject.
- Metal implants and prostheses and metal foreign objects (including those that are not ferromagnetic) can move or become detached and cause serious injury. Examples include aneurysm clips, implanted nails, splitters, insulin pumps, prostheses, cochlear implants, cardiac pacemakers, and cardiac or nerve defibrillators.
- Magnets generate strong magnetic fields that can affect the operation of magnetically sensitive devices (external devices), resulting in death or serious injury to the user. The most common item in this category is the pacemaker. A person with a pacemaker should confine themselves to areas where the magnetic field is less than 5 gausses.
- The MRI scanner can generate very high levels of acoustic noise, which may cause some patient discomfort. Earplugs can reduce noise levels by at least 25 decibels.
- One of the dangers of cryogenic gases is the extinguishing of the magnet. Quenching is the (usually unexpected) loss of superconductivity in an NMR magnet, leading to rapid heating through increased resistance to high current. The superconducting magnet contains both liquid helium and liquid helium nitrogen. A significant volume of liquid helium turns into a gas when the magnet turns off. When the magnet is off, the superconducting magnet loses its ability to superconduct and the stored energy is released as heat, which boils liquid helium. Helium gas exits the magnetic dewar and fills the space from top to bottom (helium is lighter than air), forming a cloud near the ceiling.
An extinction is evident: a large cloud of helium vapor forms over the magnet, accompanied by a loud hiss that can create an oxygen-depleted atmosphere. Extinction can forcefully damage the magnet, and ferrous objects will be attracted to the magnet hole.
How to evacuate during an emergency situation? 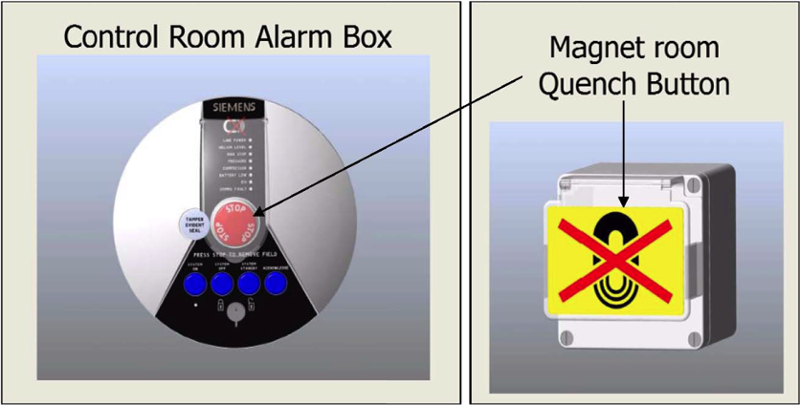 Two emergency buttons are located on each magnet:
Two emergency buttons are located on each magnet:
- Emergency Stop: Shuts off all incoming electrical power to the magnet’s power distribution unit (PDU). It is used when there is a fire, spark, loud noise, flood, or catastrophic equipment failure.
- Emergency quench or quench: Causes instantaneous collapse of the superconducting magnetic field. It is only used when a large magnetic object traps a person against the magnet and no other method can prevent further injury or free the person.
- Know the location and function of the two emergency buttons located on each magnet.
Emergency Procedures 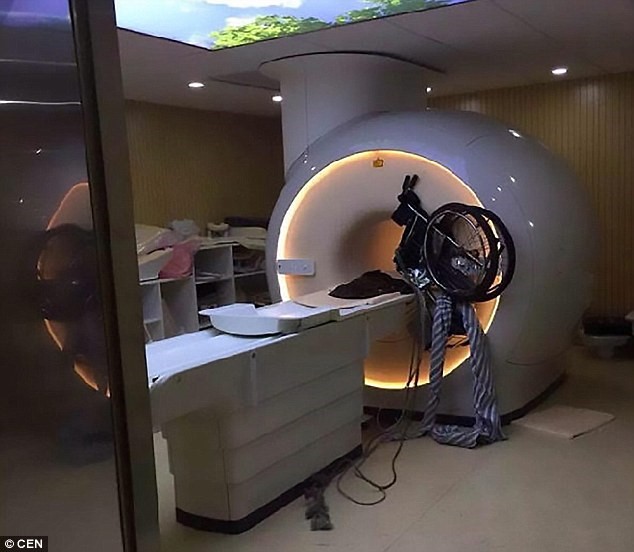 Follow those steps if a magnet quench happens or if the oxygen reveal alarm turns on:
Follow those steps if a magnet quench happens or if the oxygen reveal alarm turns on:
- Evacuate the room immediately, depart the doorways open for the duration of egress, and set off the fire alarm to evacuate the building
- Call the Emergency Number
- No one must be allowed to go into the room till helium has absolutely boiled off. ‘
- The emergency responders will investigate the oxygen awareness and offer the all- clean whilst oxygen tiers go back to normal.
- Help others get to safety.
- Contact the assigned personnel for the area.
- Available personnel must be prepared to guide and assist first responders and ensure that only MR-compatible equipment is brought into magnetic spaces.
How to help a person be trapped by a ferrous object on the MRI magnet?
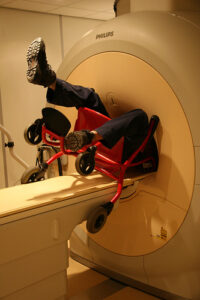
Follow these steps if someone is trapped by a ferromagnetic object on the magnet:
- Rescuers entering the magnet room must remove all metal without exception. Access to the room is restricted to people with non-removable metal, such as pacemaker or an implanted device prohibited. Limit access to necessary personnel. Determine if the object holding the victim can be removed without causing further injury.
- If the extraction is successful, immediately evacuate the victim to an area outside the MR machine room and prevent others from entering the room. A ferromagnetically assisted resuscitation can be performed once the victim has left the machine room.
- When there is a life-threatening emergency, and there is no other way to extricate the victim without removing the magnetic field, a magnet quench must be initiated by pressing the shutdown or emergency tour button to create a hazardous environment. Expect a loud noise from the cryogen outlet and the release of dense white mist. As the magnetic field decreases, the object the victim is holding may fall and cause more damage.
- Also, it should be assumed that spills from surfaces are oxygenated and treated as a fire hazard. Do not perform this procedure unless you are prepared to evacuate the victim and yourself as soon as the room becomes depleted of oxygen.
Only follow these remaining steps if rapid cool down is required:
- Open the door to the magnet room as the pressure created by the rapid cool down may prevent the doors from opening. Do not allow others to enter the room through the open door.
- All personnel should know to leave the room and not return until the helium has dissipated and the room can be safely reoccupied. Detectable.
Kryptonite Solutions

 Two emergency buttons are located on each magnet:
Two emergency buttons are located on each magnet:  Follow those steps if a magnet quench happens or if the oxygen reveal alarm turns on:
Follow those steps if a magnet quench happens or if the oxygen reveal alarm turns on:
